Email List Segmentation is one of the modern marketing techniques that allow companies to pander to their target customers. Companies with their products and services...
What’s the one marketing technique that most businesses use today? There are many. But what most firms use today for lead generation that produces accurate and ample leads in no time is email marketing. Data gathering becomes more manageable, and information spreads faster when organizations use email marketing as their strategy. Email marketing also gives users a more flexible way for companies to connect with their audience personally. The digital world can be tricky since customer tastes and algorithms constantly change. According to Statista, there will be 4.6 billion email users in 2025. This gives companies more opportunities to enhance their campaigns. But no matter how well-crafted an email is, there will always be a bounce rate. And what is a bounce rate? Sometimes, you might wonder what happens during your email marketing process, where, after sending it out, you’ll check the analytics of the email. Did the target audience open it? Is it sent to the trash? This is where the email bounce rate occurs. Tune in to this blog to understand how bounce rate happens, the different types, how to reduce it, and more.
What is the Email Bounce Rate
Email marketers use a metric tool to measure how many emails could not reach the recipients’ inboxes for various reasons, and this is what we call the email bounce rate. Some of the email addresses on your list may bounce when sending an email campaign. This means that the email couldn’t reach the right recipient. Email campaigns must have a low bounce rate as much as possible to ensure success. Moreover, as email marketers, you must be able to monitor bounce rates for various reasons so you can see how effective your email marketing campaigns are. 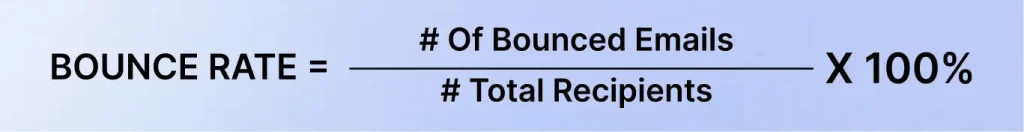
Why Monitor Bounce Rate
Here are some of the reasons why you should keep an eye on email bounce rates:
Email Deliverability
- Maintaining sender reputation: ISPs (Internet Service Providers) give you a score showing your trustworthiness as an email writer. If you have a high bounce rate, that score will go down. If you have a bad image as a sender, your emails could be marked as spam, making them less valuable.
- Avoiding spam traps: ISPs sometimes change old or wrong email addresses into “spam traps.” If you send emails to these addresses, it will hurt your image as a sender.
Data Quality
- Database accuracy: A high bounce rate often indicates that your email list requires an update or better handling. Keeping track helps you keep a clean, up-to-date database, improving your email marketing ROI (Return on Investment).
- Segmentation and personalization: If you know which emails aren’t being delivered, you can better divide your viewers into groups. If you know your texts are going to the right people, you can personalize them better.
Cost Efficiency
- Financial implications: Many email services charge you based on how many texts you send. It’s a waste of time and money to send emails that bounce back.
- Bandwidth usage: Both you and your ISP lose data and resources for every email that bounces. Everyone would benefit from reducing this as much as possible.
Engagement Conversion
- Improved metrics: When you eliminate bounced email addresses, metrics like open rates, click-through rates, and conversion rates are more accurate. Knowing this, it is easier to make decisions and curate new strategies.
- Customer engagement: In case your prospective customers don’t receive your emails, it becomes harder to connect with them. You can monitor bounce rates as quickly as possible to get them back on track.
Legal Compliance
- Compliance with regulations: ISPs and government agencies are very concerned about emails not being asked for. If you have a high bounce rate, especially to spam traps, you could be breaking laws like the CAN-SPAM Act in the U.S. or the GDPR in Europe, which could cost you a lot of money in fines.
Proactive Issue Resolution
- Troubleshooting: When you monitor bounce rates, you can quickly figure out the error before it worsens. Soft bounces may let you know about short-term problems that can be fixed quickly, like a computer that is down that you might not have noticed otherwise.
As email marketers, you must take the initiative to observe and reduce email bounce rates because it helps ensure that the messages are sent to the correct email addresses, saves you more money, protects your image, and increases sales and engagement.
Email Bounce Types
Email marketing works best when you know how often your emails get sent back. Managing your email list and following best practices are good ways to reduce bounce rates and make email campaigns more effective. But first, you need to understand the two bounce rates you will encounter in your campaigns—hard bounce and soft bounce.
Hard Bounces
Hard bounces are emails that are rejected forever by the recipient’s mail server. Hard bounces mean that the email can’t be sent under any circumstances. This is different from soft bounces, which may only be temporary. Different factors cause these hard bounce rates, such as:
- Invalid email address: There is no email address with that name. It could be because the email address was mistyped, or it could be made up.
- Domain doesn’t exist: The part of the email address after the ‘@’ sign (the domain name) doesn’t exist or is written incorrectly.
- Email server blocks sender: Some email systems are configured to block specific senders or domains from sending emails. In this case, emails from these senders or domains will always be refused.
- Deactivated account: The user or the email service provider may have deactivated or disabled the email account.
- Syntax errors: The email address may be incorrect because it contains spaces or is missing the ‘@’ symbol.
- Policy reasons: Policies set by a company or ISP can sometimes cause emails to bounce hard, especially if they are marked as spam or otherwise violate the policies.
According to Constant Contact, as of December 2022, here are the average email open and clickthrough rates by industry. You can recognize the hard bounce rates per industry in this table.
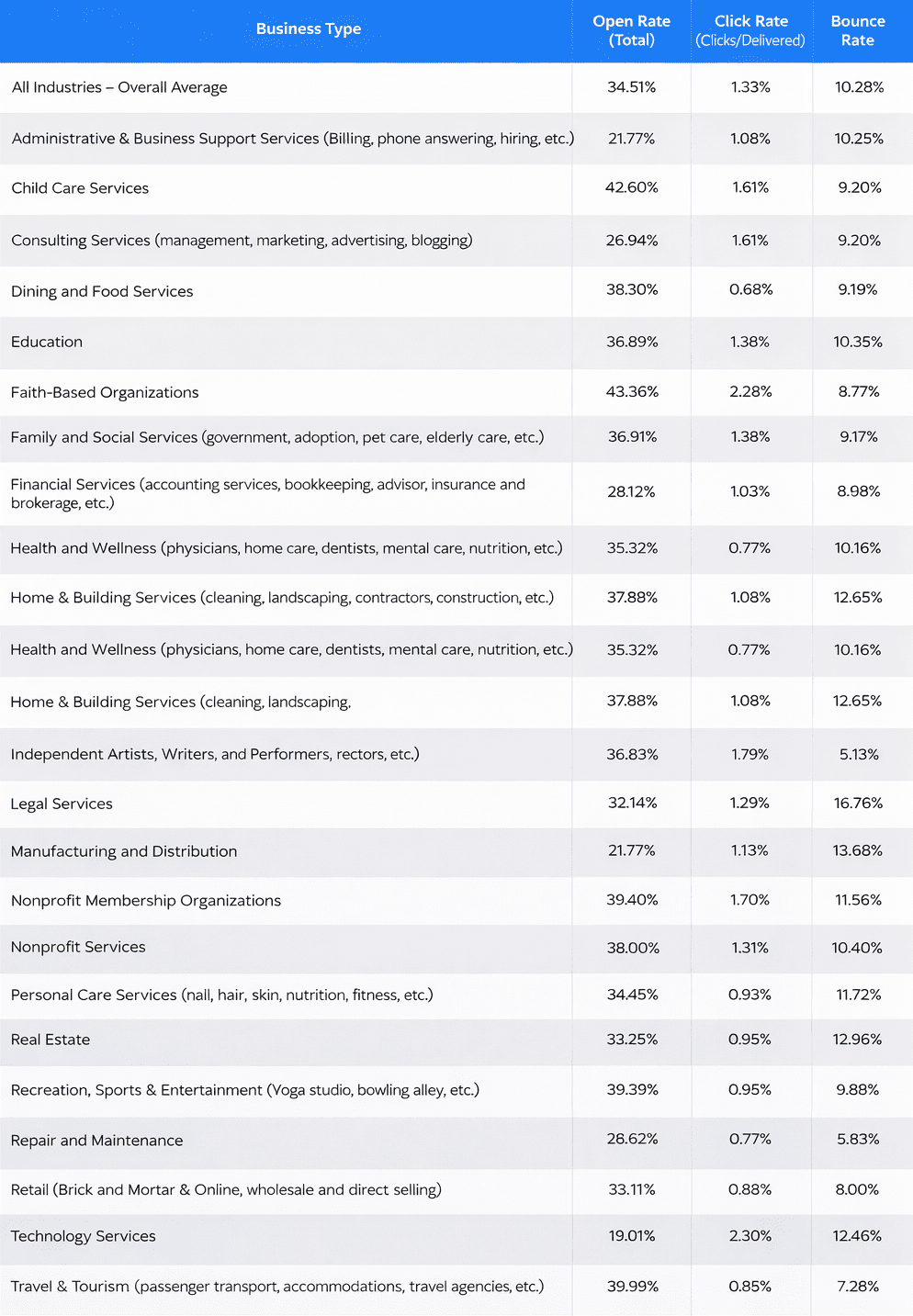
Email open, click, and bounce rate based on industries.
Soft Bounces
Soft bounces are emails that reach the recipient’s mail server but are returned before they reach the intended recipient’s account. Hard bounces are lasting and need to be fixed right away. Soft bounces, on the other hand, are usually temporary and can be fixed without taking the email address off your mailing list. Different factors cause soft bounces, like:
- Full mailbox: If the recipient’s inbox is full, new emails may be temporarily held until space is available.
- Server downtime: Emails may be returned if the recipient’s email server is temporarily down or experiencing problems.
- Large message: If the email message or its attachments exceed the size limit set by the recipient’s server, the email may bounce back.
- Time-out: Emails may be returned if they cannot be delivered within a set period, usually determined by the recipient’s mail server.
- Greylisting: To stop spam, some email servers use “greylisting” to briefly block emails from unknown or suspicious sources.
- Temporary blocking: An email address or IP address may be temporarily blocked due to suspicious behavior, but this usually resolves on its own.
Also Read What is BIMI?
While all of these happen, most email deployment platforms will try to resend an email that has “soft bounced” a certain number of times before it is considered a “hard bounce” and removed from the list of emails to send.
Bounce Rate and Email Deliverability Rates
Email deliverability and email bounce rate are closely linked. A high bounce rate can significantly affect email delivery. Here are some reasons why:
Impact on Sender Reputation
- Poor score: Email service providers (ESPs) and Internet service providers (ISPs) assign sender scores based on various metrics, including your bounce rate. Your source score can go down if you have a lot of bounces.
- Blacklisting: If your bounce rate is too high, your IP address or website could be on a blacklist. This would make it almost impossible for your emails to get to anyone’s inbox.
- ISP filters: If you have a lot of bounced emails, ISP filters may mark your future emails as spam, making it harder for people to get them.
Impact on Engagement Metrics
- Open rates go down: If your emails aren’t getting sent, no one will open them, so your open rates will go down. This, in turn, can hurt your reputation as a sender, creating a vicious cycle.
- Reduced click-through rates: Fewer people will open your emails and read your content if they don’t reach the right people.
Impact on Future Campaigns
- Learning curve: When bounce rates are high, it can be hard to tell how well different email tactics work. This might mess up A/B tests and other metrics.
- Waste of resources: If many emails aren’t sent, the time and work that went into making those emails is lost.
- List hygiene: If an email is hard to send, it may indicate that the list needs cleaning and may possibly affect other efforts if you don’t resolve the problem.
Legal Consequences
- Compliance issues: Consistently high bounce rates could violate laws like the CAN-SPAM Act in the U.S. or the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the EU, which have rules about sending to bogus or inactive email addresses.
Addressing the Issue
- List cleanup: Regularly updating your email list to remove incorrect or unresponsive addresses can lower your bounce rate.
- Content review: Check your emails’ content to ensure they don’t look like spam. This will increase the likelihood that they will be delivered.
- Monitoring and feedback: Monitor your bounce rates with analytics and make changes as needed.
What is an Acceptable Bounce Rate?
Every email marketer needs to worry about their email’s bounce rate. If your hard bounce rate is too high, it can hurt your email delivery rates in a big way. No matter your business, you should keep your standard email bounce rate under 2%. This is the rate that internet service providers (ISPs) have decided is okay to help people distinguish between good email content and spam. ESPs have to follow this standard for the email return rate. You will get an email warning if you continue to bounce more messages than allowed.
Interpreting Bounce Rate Results
The email bounce rate tool will tell you your bounce rate after you enter your information. One of three groups will be made up of your results.
- 2% or lower – A reasonable bounce rate
- 2.1% or 5% – higher than the normal
- 5.1% or higher – The email list needs attention, and the bounce rate is too high.
This is where an email bounce rate calculator comes in.
Measuring your email’s return rate is a low-lift solution to maximize your email marketing strategies. When you understand how to calculate it and the whole metric, you can now proceed to make smart choices to advance your campaigns, protect the sender’s reputation, and offer you a better ROI.

There will be some bounces, but you can keep your email bounce rate below the suggested standard by sending emails consistently. After you send out your next email campaign or newsletter, watch important email marketing data like open rates, clicks, and bounces. If you look into why those bounces are happening and find that some of your email addresses no longer work, you can take them off your email list. On the other hand, sending out email messages randomly makes it more likely that more invalid email addresses will be sent. Keep your email list clean and uniform to keep the bounce rate low. You can help keep your average email bounce rate low by authenticating your address. Email authentication is a way for ISPs to determine if an email message came from an actual, authorized sender from its linked domain. Some of these ways to verify an email address are
- Domain-Based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance (DMARC)
- Domain Keys Identified Mail (DKIM)
- Sender Policy Framework (SPF).
By creating and using these email authentication records, you can prove you are who you say you are and reduce the number of times your emails bounce. Double opt-in is also a popular way to sign up for emails because it ensures the email is accurate. This is how it works:
- A person uses their email address to sign up on your registration form.
- You send a proof email to the address right away. The person checks to make sure that they want to get an email.
- You get proof that the address is correct and that you can send emails to it without worrying that they will bounce.
Without a double opt-in, anyone can sign up with a fake email address, and you won’t find out until an email bounces.







