According to research, email marketing offers the highest return on investment among all marketing strategies. To put it into perspective, you can get $36 for...
Key Takeaways
- Email size limits apply to the complete message, including body text, inline images, and all attachments combined.
- Email encoding (Base64) increases file sizes by about 37%, so a 20MB attachment becomes 27.4MB when transmitted.
- Gmail allows a 25MB total message size, Outlook ranges from 20-34MB depending on the version, and Yahoo limits attachments to 25MB.
You attach a 28MB presentation to an email and hit send. But, it bounces right back with an error: “Message size exceeds maximum allowed.” You compress the file down to 24MB, try again, and… same result. The file looks small enough, but email size limits don’t work the way most people assume they do.
Email providers set strict limits for a reason. Server capacity, bandwidth, and reliable delivery at scale all factor in. Those limits also vary by provider and account type, but they all share one important detail: the limit applies to the entire message, not just the attachment. So that 20MB file, plus the email text, any inline images, and the extra overhead added during encoding, can quietly push the message over the edge, even when the attachment itself seems fine.
Once you understand how email file size limits actually work, you can avoid failed sends, repeated bounces, and wasting time trying to push files through email that were never going to make it. This guide explains what those limits really measure, how different providers handle oversized messages, and which options work best when a file is simply too large for email.
What Is an Email File Size Limit?
An email file size limit is the maximum amount of data that can be transmitted in a single email message. This limit encompasses everything included in the email, not just file attachments.

- Attachment files. Any files you attach, including documents, images, videos, and spreadsheets, count toward the total size. Multiple attachments are added together.
- Email body text. The text content of your email contributes to the total, though it’s usually negligible (a few kilobytes) compared to attachments. HTML-formatted emails with styling take slightly more space than plain text.
- Inline images. Images embedded directly in the email body (signatures, logos, or images placed within the message text) add to the total size, often without users realizing it.
- Encoding overhead. Email systems encode binary files (images, PDFs, or videos) into text format for transmission using Base64 encoding, increasing file size.
Typical limit ranges
Most major email providers enforce limits between 20 and 25MB for total message size. Business email servers often set limits between 10 and 35MB, depending on company IT policies. Smaller or self-hosted email providers may cap messages at 10MB or less to conserve server resources.
Email File Size Limits by Popular Email Providers
Different email providers set different limits based on their infrastructure and user base. Understanding these limits helps you know when to switch to alternative file-sharing methods.
Gmail
Limit: 25MB total message size when sending
Gmail enforces a strict 25MB limit on the total size of sent emails, including all attachments, email body, and encoding overhead.
How Gmail handles oversized attachments
When you try to attach files larger than 25MB, Gmail uploads them to your Google Drive automatically and inserts a shareable link in the email instead. Recipients receive the link and can download files directly from Drive, bypassing email size limits entirely.
This happens automatically; you don’t manually upload to Drive or generate links. Gmail handles the process and notifies you that your files were too large for direct attachment.
Yahoo Mail
Limit: 25MB for attachments
Yahoo Mail allows attachment files up to 25MB, similar to Gmail. When you try to attach larger files, Yahoo offers to use Dropbox integration for file sharing instead.
Unlike Gmail’s automatic Drive upload, Yahoo requires you to connect your Dropbox account and authorize file uploads. Once connected, oversized files upload to Dropbox, and a link is inserted in your email.
If you haven’t set up Dropbox integration, Yahoo simply prevents you from attaching files that exceed 25MB, requiring you to manually reduce file size or use an alternative sharing method.
Outlook.com (Hotmail)
Limit: 20MB to 34MB, depending on version
Outlook.com’s attachment limits have evolved over time. Older accounts or interfaces enforce a 20MB limit, while newer versions allow up to 34MB total message size in some configurations.
OneDrive integration
Like Gmail’s Drive integration, Outlook automatically uses OneDrive when attachments exceed size limits. Files upload to your OneDrive, and recipients receive a link for downloading rather than direct attachments.
This works smoothly for users with Microsoft accounts and OneDrive access, though some corporate environments restrict OneDrive usage, preventing this automatic fallback.
Microsoft Exchange (Business Email)
Limit: Typically 10MB default, often increased to 25-35MB
Microsoft Exchange servers used by businesses have configurable size limits set by IT administrators. The default limit is often 10MB, which is restrictive compared to consumer email providers.
Many organizations increase this to 25MB or 35MB to match employee needs, but limits vary widely depending on company infrastructure, storage capacity, and email policies.
Why business limits differ
Corporate IT teams balance employee convenience against server costs, security concerns, and compliance requirements. Higher limits require more storage and bandwidth, so organizations with tight budgets or limited infrastructure keep limits lower.
If you’re sending email through a corporate account and hitting size limits, check with your IT department about current policies and whether limits can be adjusted for legitimate business needs.
Other email providers and servers
Smaller regional providers, educational institutions, and self-hosted email servers often set stricter limits than major providers.
Common limit ranges for smaller providers:
- 10MB: Common for budget hosting providers and older systems
- 15MB: Moderate limit for mid-tier providers
- 5MB or less: Rare but exists on very limited infrastructure
Configurable limits
Self-hosted email servers (running software like Postfix, Exim, or Exchange) have administrator-configurable limits. System administrators can set any limit based on available storage, bandwidth, and organizational needs, though most follow industry norms of 20-35MB to avoid compatibility issues with external recipients.
Why Email Providers Set File Size Limits
Email size limits exist for technical, operational, and reliability reasons that affect both providers and users.

Server storage and bandwidth constraints
Email servers store copies of every sent and received message. Allowing unlimited attachment sizes would overwhelm storage infrastructure quickly, especially with millions of users sending large files daily.
Bandwidth is similarly constrained. Large attachments consume network capacity when transmitted, slowing delivery for all users during peak times. Limiting message sizes ensures consistent delivery speeds across the entire user base.
Reliability and performance at scale
Smaller messages transmit faster and more reliably than large ones. Network interruptions, server issues, or connection problems are less likely to cause failures with 5MB messages than with 500MB transfers.
Email protocols (SMTP) weren’t originally designed for large file transfers. While modern implementations handle larger messages, the protocol works best with smaller payloads, making size limits a practical concession to underlying technology constraints.
Encoding overhead increases file size
Binary files (images, PDFs, videos, ZIP archives) must be encoded into text format for email transmission using Base64 encoding. This encoding process increases the file size by approximately 37%.
Example calculation:
- Original file: 20MB
- After Base64 encoding: 20MB × 1.37 = 27.4MB
- A 20MB attachment becomes a 27.4MB email
This overhead means a 20MB file actually consumes 27.4MB of your size limit, explaining why emails sometimes bounce even when attachments appear to be under the stated threshold.
Deliverability and system stability
Following email delivery guidelines from major providers helps ensure messages reach inboxes reliably. Size limits are one component of broader deliverability best practices that keep email systems stable and performant.
Email deliverability statistics show that smaller, properly formatted emails consistently achieve better inbox placement than large, attachment-heavy messages that stress receiving servers.
What Happens When an Email Exceeds the File Size Limit
Oversized emails fail in several ways, depending on where in the transmission process the limit is exceeded.
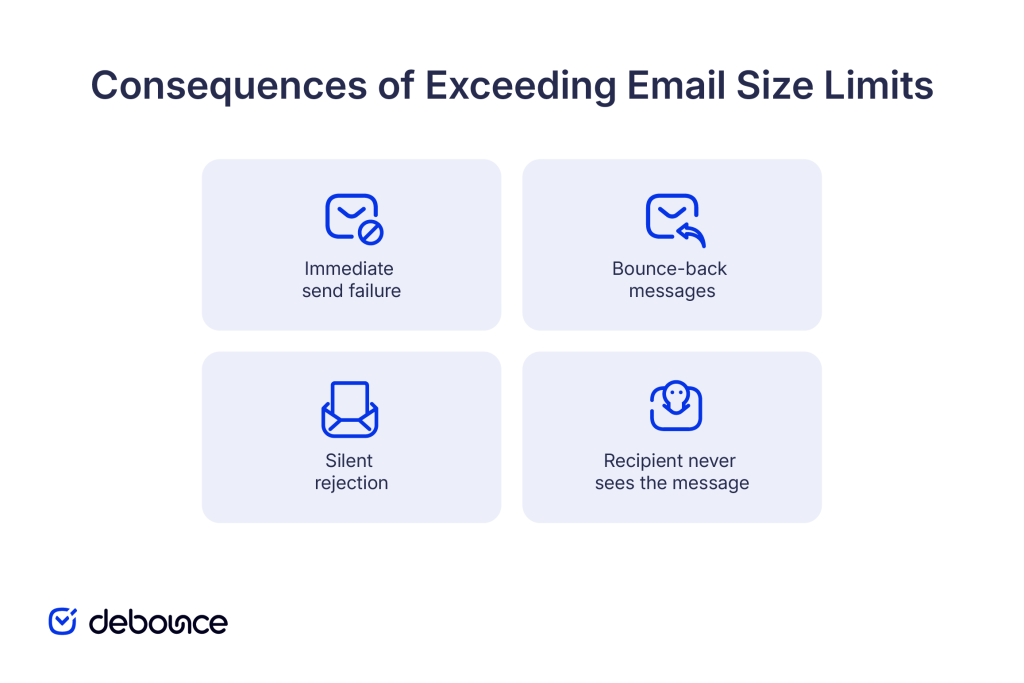
Immediate send failure
Most modern email clients check message size before attempting to send. If your email exceeds the provider’s limit, you’ll receive an immediate error message: “Message size exceeds maximum allowed” or “Attachment too large.”
The email never leaves your outbox, and you can remove or compress attachments before trying again.
Bounce-back messages
If your email client doesn’t catch the size issue and attempts to send, the receiving mail server may reject the message and return a bounce notification. These bounced emails explain that the message exceeded size limits and couldn’t be delivered.
Bounces add to your overall bounce rate, potentially affecting sender reputation if they occur frequently across campaigns. Understanding average bounce rate by industry helps you gauge whether size-related bounces are becoming a pattern.
Silent rejection
In some configurations, oversized emails are rejected without notification. The message disappears from your sent folder, but neither you nor the recipient receives confirmation or error messages. This is the worst scenario because you believe the email was sent successfully, but the recipient never receives it and has no way to know you tried to contact them.
Recipient never sees the message
Regardless of how the failure occurs, the outcome is the same: recipients never receive oversized emails. No partial delivery occurs. Either the complete message arrives, or nothing does.
How to Send Large Files Without Hitting Email Limits
When files exceed email size limits, use methods designed for large file transfers rather than forcing attachments through email.
Cloud storage links
Upload files to Google Drive, Dropbox, OneDrive, or similar services, then share links via email instead of attaching files directly. This approach:
- Bypasses all email size limits
- Gives you control over access permissions and expiration
- Works reliably for files of any size
- Allows recipients to download at their convenience
File-sharing services
Dedicated file transfer services like WeTransfer, Send Anywhere, or similar platforms specialize in large file transfers. Upload your file, enter the recipient’s email, and they receive a download link.
These services typically support files much larger than email limits (2-100GB depending on the service and plan) and automatically handle delivery without requiring manual cloud storage management.
File compression
Compressing files into ZIP archives can reduce their size enough to fit under email limits, but this only works for certain file types.
What compresses well:
- Text documents (50-70% reduction)
- Uncompressed images (10-30% reduction)
- Multiple small files bundled together
What doesn’t compress:
- Videos (already compressed)
- JPG/PNG images (already compressed)
- MP3 audio (already compressed)
- PDF files (moderate compression at best)
If compression doesn’t reduce your file below email limits, switch to cloud links rather than spending time trying to compress further.
Maintain email list quality
Even when messages stay under size limits, they fail if sent to invalid addresses. Using email list validation before sending ensures emails reach real, active recipients rather than bouncing due to address issues.
Email list monitoring continuously tracks list health over time, automatically flagging addresses that become invalid so your messages, regardless of size, consistently reach intended recipients without delivery failures.
Wrapping Up
Email file size limits typically range from 20-25MB across major providers, with these limits applying to total message size, including attachments, body text, inline images, and encoding overhead that increases file sizes by approximately 37%. Understanding these limits helps you avoid bounced emails and failed sends caused by oversized messages.
When files exceed limits, cloud storage links provide the most reliable sharing method for any file size. Gmail, Outlook, and Yahoo all offer automatic cloud integration that switches oversized attachments to shareable links without requiring manual uploads.
Regardless of file size, you need to ensure your emails reach valid addresses. Use DeBounce to verify email lists before important sends, removing invalid addresses that would cause bounces. Clean lists support better deliverability and protect sender reputation across all your email communications.






